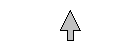














![pict1672.jpg [140x193]](pict1672.jpg) Charles Martel At Tours [c. 1880 Steel Engraving ]
Charles Martel At Tours [c. 1880 Steel Engraving ] |
Mayor of the Palace of Austrasia 714-741
Mayor of the Palace of Neustria 719-720
Mayor of the Palace of Burgundy 719-720
Charles Martel became Mayor of the Palace of Austrasia when his father, Pepin II, died in 714. That year he was imprisoned by his step-mother Plectudis, but escaped later in the year to lead the Austrasian and Neustrian nobles. The next year, the new King Chilperic II refused to act as a puppet to the nobles, and was backed by the Aquitaine duke Eudo, who was by then semi-independent from Frankish sovergnty. In 719, Charles defeated Eudo and took Chilperic hostage. Eudo's terms for mercy were that Chilperic would be recognized as sole ruler of the Franks, and the Charles would control all royal offices (i.e. as Mayor). Eudo had no other choice but to accept. In 720, Chilperic II died, Theuderic IV became king, Charles was stripped of his positions, Eudo was able to attain full independence, and Charles was preoccupied with pushing back Saxon invaders across the Rhine.
The next year, Eudo defeated the advancing Moslem armies and made peace with them, however in 725 they attacked Septimania and invaded Burgundy, drawn by the wealth of the Catholic Church. In 731, the Spanish governor Abd ar-Rahman, much loved by the Moslem people, invaded and easily overran all of Aquitaine. The next year he took Poitiers and marched to Tours, where he was soundly beaten by Mayor Charles, and Rahman was killed in the battle. Three years later Eudo died, and Charles took supreme control of Gaul. In 737, Provence invited back the Moslems, who were defeated by Charles and his younger brother Hildebrand, then pushed out of Gaul forever. In 741, Charles died.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Charles Martel - Latin CAROLUS MARTELLUS, German KARL MARTELL (b. c. 688--d. Oct. 22, 741, Quierzy-sur-Oise, France), mayor of the palace of Austrasia (the eastern part of the Frankish kingdom) from 715 to 741. He reunited and ruled the entire Frankish realm and stemmed the Muslim invasion at Poitiers in 732. His byname, Martel, means "the hammer."
Charles was the illegitimate son of Pepin of Herstal, the mayor of the palace of Austrasia. By this period the Merovingian kings of the Frankish realm were rulers in name only. The burden of rule lay upon the mayors of the palace, who governed Austrasia, the eastern part of the Frankish kingdom, and Neustria, its western portion. Neustria bitterly resented its conquest and annexation in 687 by Pepin, who, acting in the name of the king, had reorganized and reunified the Frankish realm.
The assassination of Pepin's only surviving legitimate son in 714 was followed a few months later by the death of Pepin himself. Pepin left as heirs three grandsons, and until they came of age, Plectrude, Pepin's widow, was to hold power. As an illegitimate son, Charles Martel was entirely neglected in the will. But he was young, strong, and determined, and an intense struggle for power at once broke out in the Frankish kingdom.
Both Charles and Plectrude faced rebellion throughout the Frankish kingdom when Pepin's will was made known. The king, Chilperic II, was in the power of Ragenfrid, mayor of the palace of Neustria, who joined forces with the Frisians in Holland in order to eliminate Charles. Plectrude imprisoned Charles and tried to govern in the name of her grandchildren, but Charles escaped, gathered an army, and defeated the Neustrians in battles at Amblève near Liège (716) and at Vincy near Cambrai (717). His success made resistance by Plectrude and the Austrasians useless; they submitted, and by 719 Charles alone governed the Franks as mayor.
Assured of Austrasia, Charles now attacked Neustria itself, finally subduing it in 724. This freed Charles to deal with hostile elements elsewhere. He attacked Aquitaine, whose ruler, Eudes (Odo), had been an ally of Ragenfrid, but Charles did not gain effective control of southern France until late in his reign. He also conducted long campaigns, some as late as the 730s, against the Frisians, Saxons, and Bavarians, whose brigandage endangered the eastern frontiers of his kingdom. In order to consolidate his military gains, Charles supported St. Boniface and other missionaries in their efforts to convert the German tribes on the eastern frontier to Christianity.
Ever since their arrival in Spain from Africa in 711, the Muslims had raided Frankish territory, threatening Gaul and on one occasion (725) reaching Burgundy and sacking Autun. In 732 'Abd ar-Rahman, the governor of Córdoba, marched into Bordeaux and defeated Eudes. The Muslims then proceeded north across Aquitaine to the city of Poitiers. Eudes appealed to Charles for assistance, and Charles' cavalry managed to turn back the Muslim onslaught at the Battle of Poitiers. The battle itself may have been only a series of small engagements, but after it there were no more great Muslim invasions of Frankish territory.
In 733 Charles began his campaigns to force Burgundy to yield to his rule. In 735 word arrived that Eudes was dead, and Charles marched rapidly across the Loire River in order to make his power felt around Bordeaux. By 739 he had completely subdued the petty chieftains of Burgundy, and he continued to fend off Muslim advances into Gaul during the decade.
Charles' health began to fail in the late 730s, and in 741 he retired to his palace at Quierzy-sur-Oise, where he died soon after. Before his death he divided the Merovingian kingdom between his two legitimate sons, Pepin and Carloman. He continued to maintain the fiction of Merovingian rule, refraining from transferring the royal title to his own dynasty. He was buried at Monastáere De Saint Denis, Saint Denis, France.
Copyright 1994-1998 Encyclopaedia Britannica
Generated by GreatFamily 2.2 update 2